The main thing to due is make sure your blood pressure and cholesterol are ok as some studies indicated that idiopathic thickening can be associated with an increased risk of stroke.
What does thickening of the heart wall mean.
In most cases the heart muscle weakens and is unable to pump blood to the rest of the body as well as it should.
Many cases of heart wall thickening in older individuals are idiopathic meaning cause unknown.
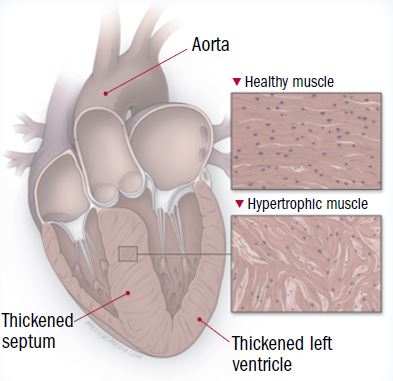
In most people with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy the muscular wall septum between the two bottom chambers of the heart ventricles becomes thicker than normal.
Find in depth information related to thickening of the heart muscle symptoms causes and treatment by going through the following article.
Testing will not easily discern a cause.
This means that for many people the symptoms remain stable during adulthood.
It can be caused by multiple factors and conditions including renal failure liver failure heart failure ascites hypoproteinemia and inflammation.
It affects people of any age notes american heart association.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is usually caused by abnormal genes gene mutations that cause the heart muscle to grow abnormally thick.
Thickening of the heart muscle myocardium occurs most commonly at the septum.
The septum is the muscular wall that separates the left and right side of the heart.
Thickening of the heart muscles is caused by a condition called hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
The thickening of the heart muscle does not tend to progress once you stop growing.
Thickening of the heart wall which is called cardiomyopathy has many causes including genetic factors long term high blood pressure damage of the heart tissue heart valve problems and metabolic disorders such as diabetes thyroid disease and obesity reveals mayo clinic.
When the heart muscles are abnormally thick it makes it very difficult for the heart to pump blood.
The thickened septum may cause a narrowing that can block or reduce the blood flow.
During this surgical procedure the surgeon removes a small amount of the thickened septal wall of the heart to widen the outflow tract the path the blood takes from the left ventricle to the aorta.
Thickening of the gallbladder wall is always abnormal although the significance of the thickening is highly dependent upon the underlying disease process.